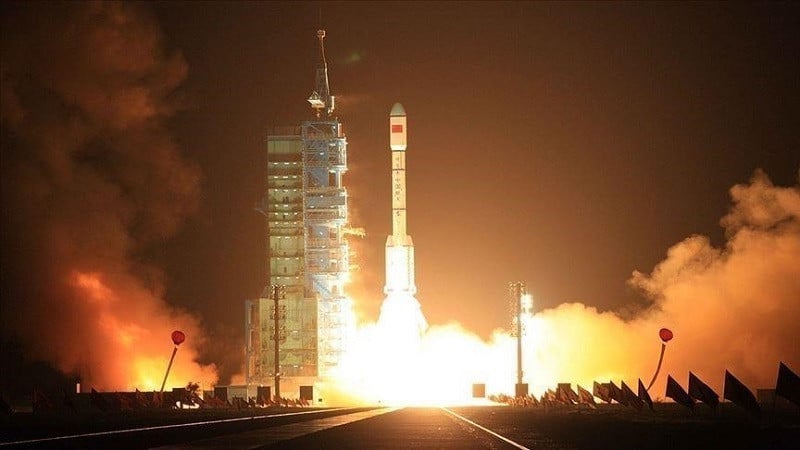
China's first commercial spacecraft launch site is ready for operations in south China's Hainan Province as of Sunday, having completed a rocket launch simulation rehearsal using its two launch pads.
According to the Hainan International Commercial Aerospace Launch Co., Ltd. (HICAL), which built and operates the launch site, the exercises performed using the launch pads included water spraying and deluge system cooling, as well as a rocket lifting arm erection test.
Following assessments, HICAL confirmed that the site is operational for launch missions.
HICAL President Yang Tianliang called on the company to work with satellite and rocket developers, and to prepare for the site's first launch mission.
Read: China's Long March-6C rocket makes maiden flight
Established in June 2022, HICAL was founded by the Hainan provincial government, the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation, the China Aerospace Science and Industry Corporation, and the China Satellite Network Group Co., Ltd.
The launch site has an approximate investment of 4 billion yuan (about 560 million U.S. dollars) and is located off the coast of Wenchang City. It includes a launch area, a TT&C (telemetry, tracking and command) building, multiple rocket assembly buildings, spacecraft testing and integration facilities, fuel storage facilities, and other structures.
It is positioned at a latitude of 20 degrees north, benefitting from the advantages of a low latitude, which increases rocket payload capacities and reduces launch costs.
Compared to inland launch sites, coastal launch sites are more convenient and safer as large rockets can transported to site by ship, which is very important for commercial launch services. A new, purpose-built port is being planned by the Hainan provincial government.
The coastal location also gives HICAL an advantage in its recovery of reusable rockets after launch. The company is working with commercial rocket developers to carry out experiments related to vertical landings and the recovery of rockets from the sea.
It said the launch site is designed with two launch pads for liquid propellant rockets and another two for solid propellant rockets, with its No.1 and No.2 launch pads completed in December 2023 and June 2024, respectively.
The No.1 pad is designed for the Long March-8, China's new generation medium-lift carrier rocket. The No.2 pad is capable of launching multiple types of rockets with various diameters from commercial rocket companies. Each pad has an annual capacity of 16 launches.
The propellant and gas supply system at the launch site is capable of refueling and supplying liquid oxygen, liquid hydrogen, kerosene and methane.
HICAL will also support commercial rocket companies in providing international commercial launch services. Xiang Dalin, vice director of HICAL's technical department, said the company will issue a universal interface file of commercial rocket designs both domestically and internationally.
The commercial space industry was included in the Chinese government work report for the first time this year. It was listed as one of the "emerging industries and future-oriented industries" that the government plans to cultivate.
According to the 2023 China aerospace science and technology blue book, the country completed 26 commercial launches in 2023, accounting for 39 percent of its total number of launches.
China's commercial space market has maintained rapid growth since 2015, with an average annual growth rate of more than 20 percent from 2017 to 2024. It is estimated that its market value will be about 2.34 trillion yuan by 2024.